Disparities in Pediatric Ophthalmology Have Increased: A Growing Concern
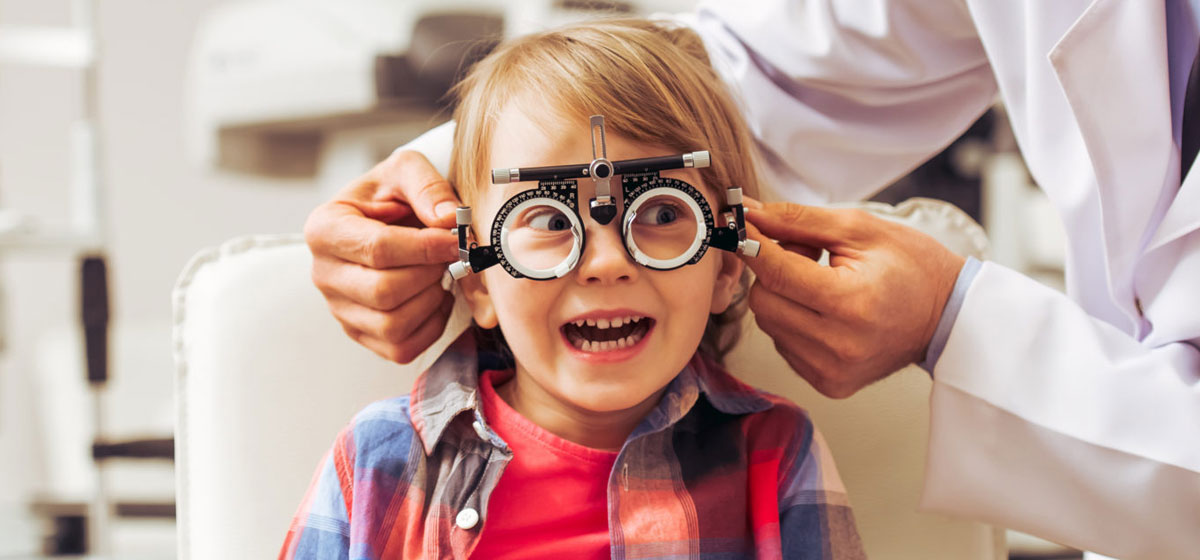
Pediatric ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases in children. It is an important specialty as eye problems in children can cause serious long-term consequences, including vision loss and developmental delays. Despite the critical nature of pediatric ophthalmology, disparities in access to care have increased in recent years, resulting in unequal treatment for children across different socioeconomic groups.
Factors Affecting the Disparities in Pediatric Ophthalmology
Access to healthcare services
One major factor contributing to disparities in pediatric ophthalmology is access to healthcare services. Children from lower-income families are more likely to live in areas with limited access to medical services, including ophthalmology care. They are also less likely to have health insurance, which makes it difficult for them to access the specialized care they need.
In addition, low-income families may not have the resources to take time off work or travel long distances to reach a pediatric ophthalmologist, further exacerbating the issue.
Language barriers
It is another factor that contributes to disparities in pediatric ophthalmology. Children from immigrant families may not speak English as their first language, making it difficult for them to communicate with their healthcare provider. In some cases, the child's parents may not be able to interpret for them, leaving the child with limited access to the medical care they need.
Racial and ethnic disparities also
They also play a significant role in pediatric ophthalmology. African American and Hispanic children are more likely to have vision problems compared to their white counterparts. However, they are also less likely to receive the specialized care they need due to a variety of factors, including limited access to healthcare services, poverty, and language barriers.
The COVID-19 pandemic
Another factor of exacerbated disparities in pediatric ophthalmology. The closure of schools and healthcare facilities has made it difficult for children to receive regular eye exams and other important medical care. In addition, many families have been economically impacted by the pandemic, making it even more challenging for them to access the specialized care their children need.
Conclusion
Disparities in pediatric ophthalmology have increased in recent years, leaving many children without access to the specialized care they need. This is a growing concern as untreated eye problems in children can have serious long-term consequences, including vision loss and developmental delays.
Addressing these disparities will require a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors, including access to healthcare services, language barriers, and poverty. Only by working together can we ensure that every child has the opportunity to receive the specialized care they need to maintain healthy vision and develop to their full potential.
Visit DocMode for courses and lectures