Effect of Temporary Cement Methods
Temporary and permanent indirect restorations are attached to the abutment teeth with a special material called dental cement. Therefore, this process is (incorrectly) called cementation or cementation.
Temporary fillings perform several important functions. Their primary role is to ensure pulp viability and provide patient comfort during the preparation of the final restoration. A properly formed and contoured provisional restoration allows the patient and dentist to assess the esthetics and function of the final restoration.
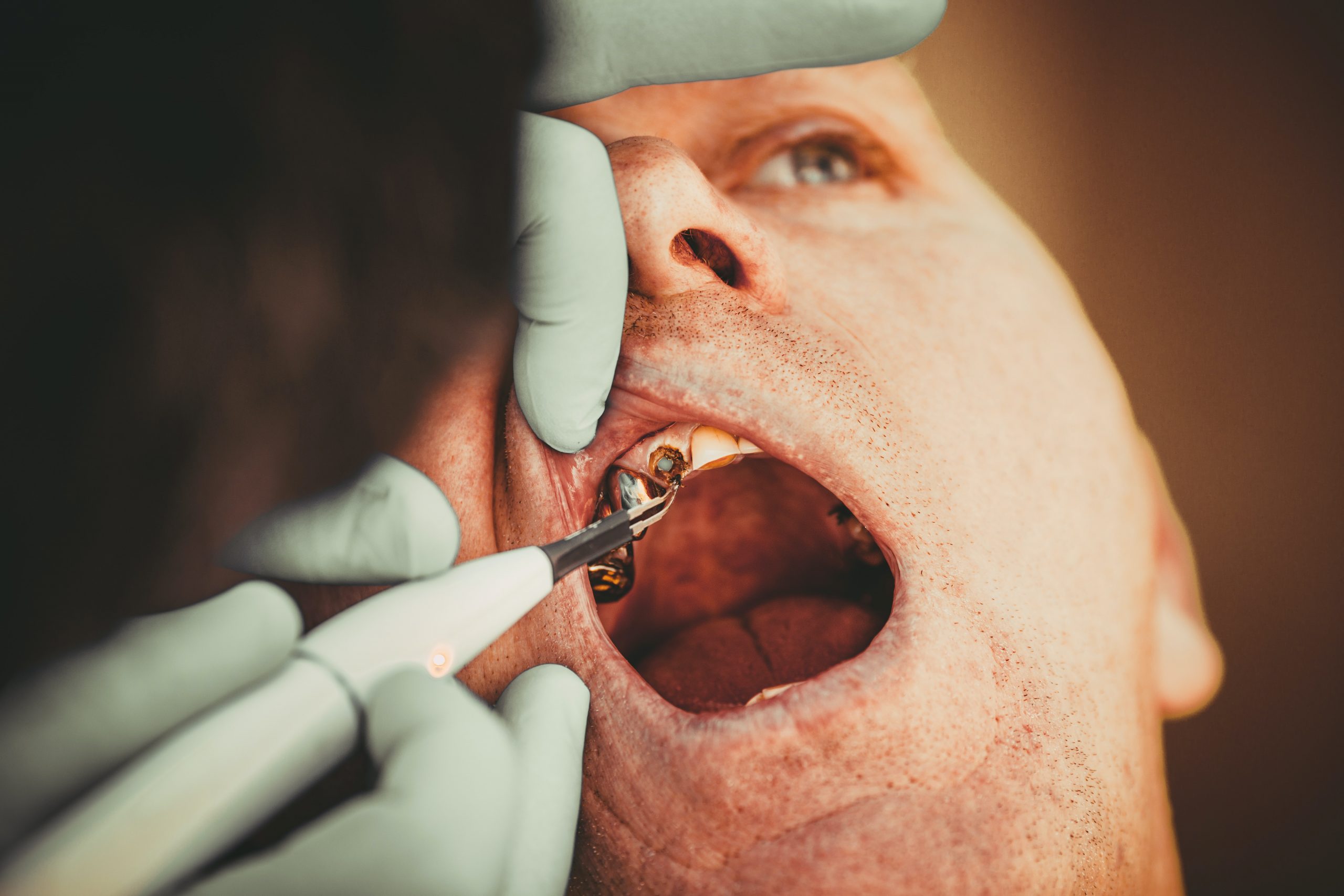
The temporary restorations also provide support and protection for the gum tissue. A temporary crown or bridge not only covers the tooth but temporarily restores tooth function. Unfortunately, a temporary prosthesis is usually made after a long visit when the doctor and patient are tired and in a hurry. Mistakes made at this stage will affect the result. The long-term maintenance of healthy pulp is the result of atraumatic preparation and the use of biocompatible restorative materials capable of sealing the restorative interface to prevent or minimize bacterial leakage.
They adhere well to teeth and prosthetic restorations. The temporary restorations are very well-cemented and easy to remove. Can protect a vitally prepared tooth and help minimize sensitivity (between visits).
Temporary cementation is used in two situations:
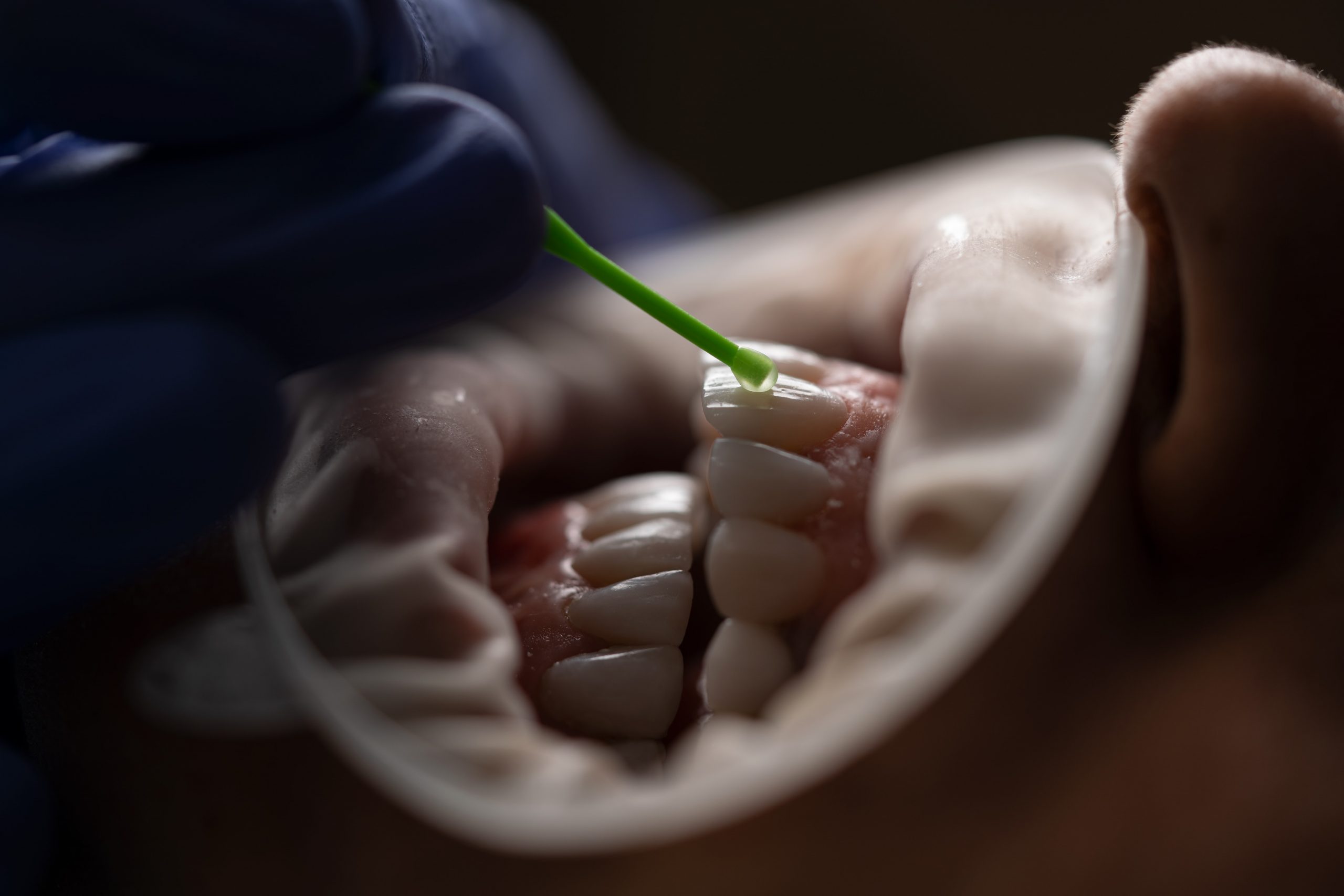
1)Preservation of temporary crowns or other temporary restorations
2)The temporary crown is usually fixed with Soft Temporary Dental Cement. This allows for easy removal when seating the final restorations and replacement between visits.
3)Temporarily cementing the final restorations
Temporary cementation in final restorations for the following reasons:
1)Assessment of the contours and margins of the filling
2)Assessment of the periodontal response of the restoration (particularly the part of the restoration that intrudes below the gingival margin)
3)check the adaptation of the tissue of the tooth to the new one
If complications arise during this period (e.g. pulpitis of the abutment tooth), the restoration can be easily removed (without destroying it), and the Condition treated