Sarcoma Awareness Month: Shining light on the ‘forgotten cancer’
Sarcoma Awareness Month raises awareness, for the need for more sarcoma research and better sarcoma therapies. Sarcoma is a type of cancer that can occur in various locations in your body (blood vessels, nerves, tendons, muscles, fat ,fibrous tissue, etc.). Sarcoma is the general term for a broad group of cancers that begin in the bones and in the soft (also called connective) tissues (soft tissue sarcoma). TYPES OF SARCOMAS.
Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of sarcoma include:
- A lump that can be felt through the skin that may or may not be painful
- Bone pain
- A broken bone that happens unexpectedly, such as with a minor injury or no injury at all
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
Diagnosis:
Sarcomas are difficult to detect and diagnose. Your doctor will study the tumor’s location using imaging scans such as simple X-rays or a CT scan. The CT scan may also involve using an injected dye to make the tumor easier to see. Your doctor may also order an MRI, PET scan, or an ultrasound.
Who is at risk for developing a soft tissue sarcoma?
- Genetic risk factors - Some inherited or acquired DNA mutations, or defects, can make you more prone to developing a soft tissue sarcoma.
- Toxin exposure - Exposure to certain toxins, such as dioxin, vinyl chloride, arsenic, and herbicides that contain phenoxyacetic acid at high doses may increase your risk of developing soft tissue sarcomas.
- Radiation exposure - especially from radiation therapy, can be a risk factor. Radiation therapy often treats more common cancers such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, or lymphomas. However, this effective therapy can increase your risk of developing certain other forms of cancer, such as a soft tissue sarcoma.
Usually, The cause of a sarcoma isn’t identified, they just appear.
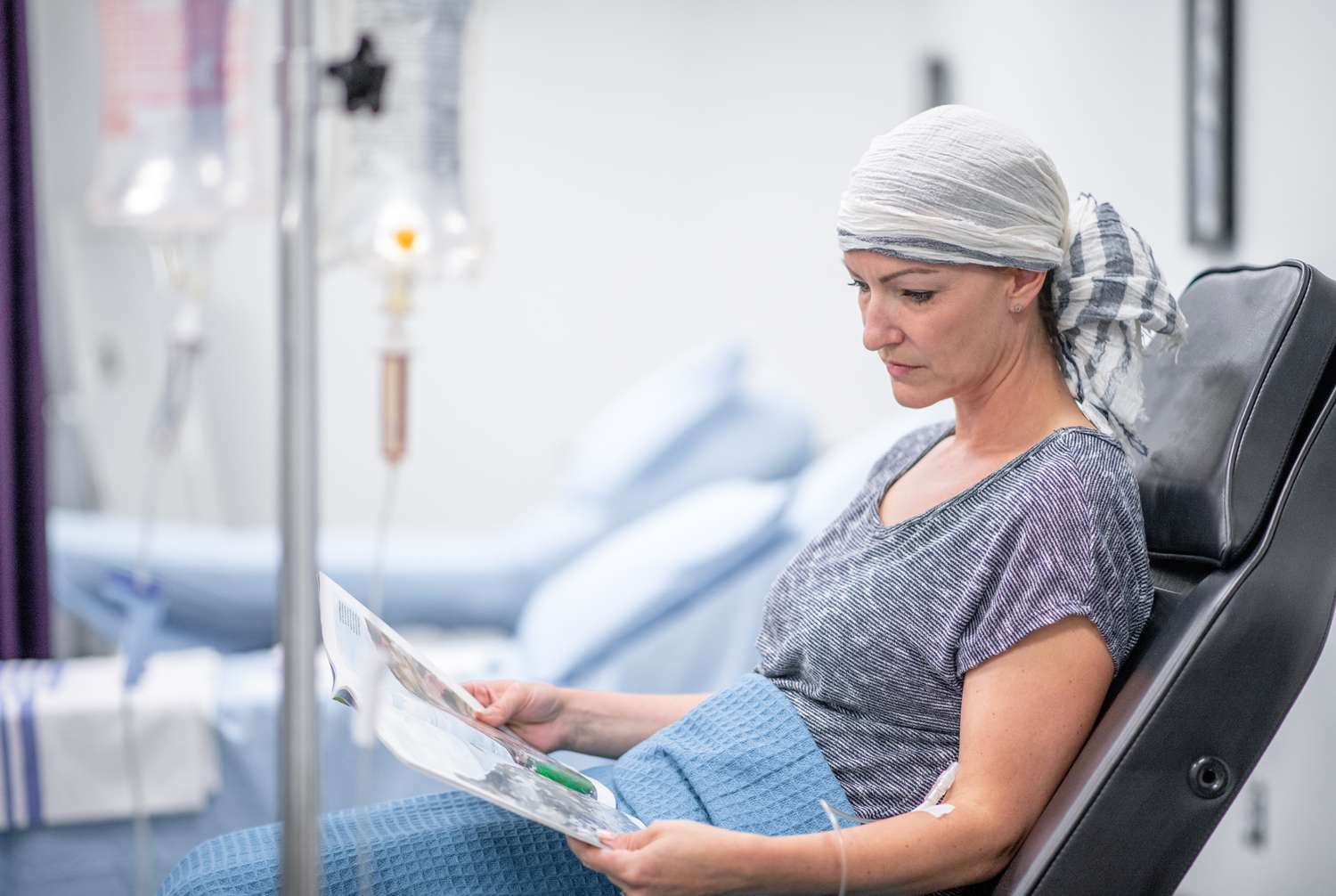
What are the treatments?
Treatment depends on the location of the tumor and the exact cell type that the tumor originated from (for example, muscle, nerve, or fat). If the tumor has metastasized, or spread to other tissues, this also affects treatment. There are side-effects and a lot of risks involved during or after the treatment.
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy