Root Canal Preparation Techniques and How to Avoid Procedural Errors in Endodontics
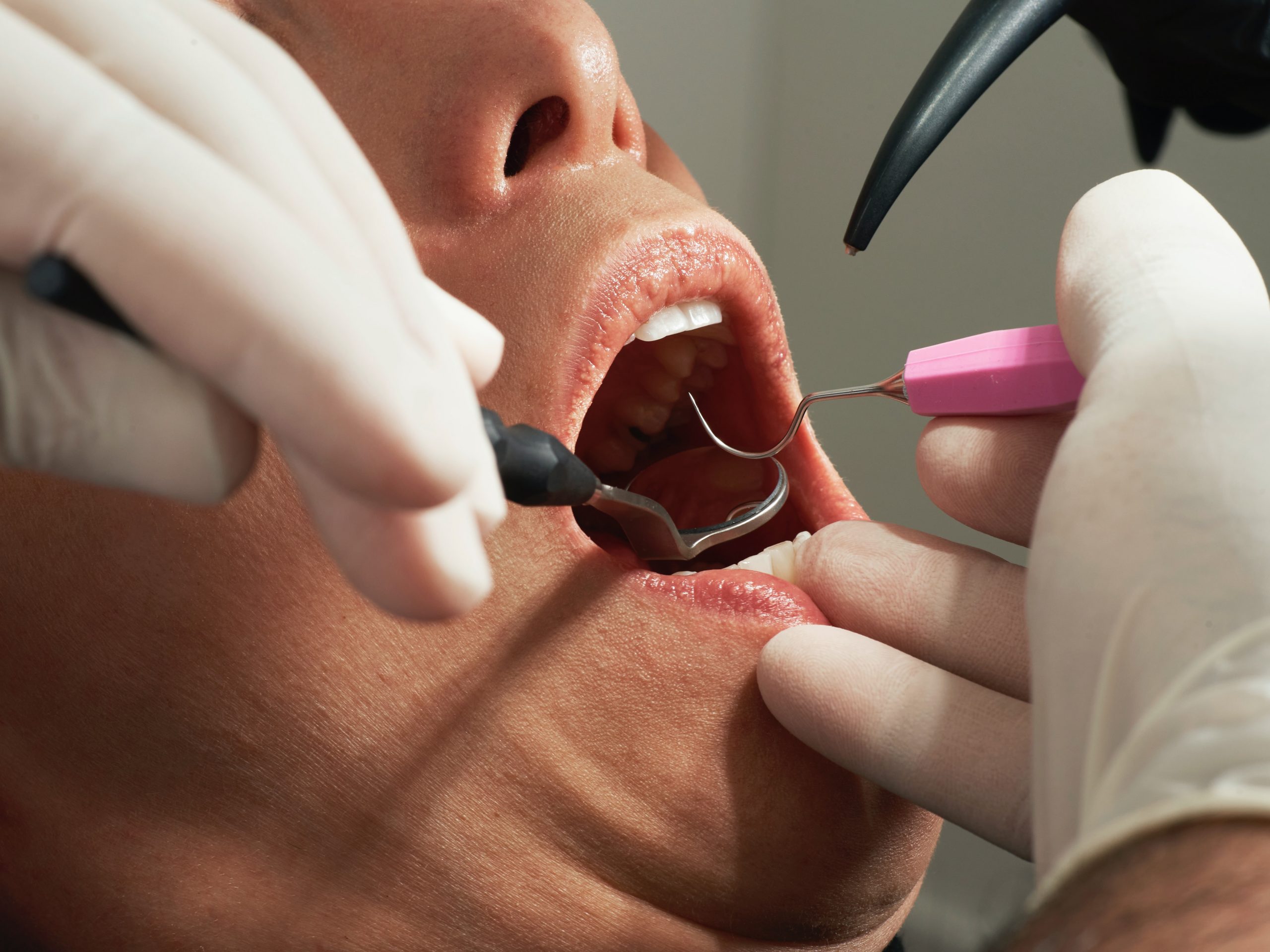
A root canal is a treatment to repair and preserve a badly decayed or infected tooth .During a root canal, the nerve and pulp of the tooth are removed and the inside is cleaned and sealed . Left untreated, the tissues surrounding the tooth become inflamed and an abscess can form. Root canals have a reputation for being painful. But the procedure itself is no more painful than putting in a filling.
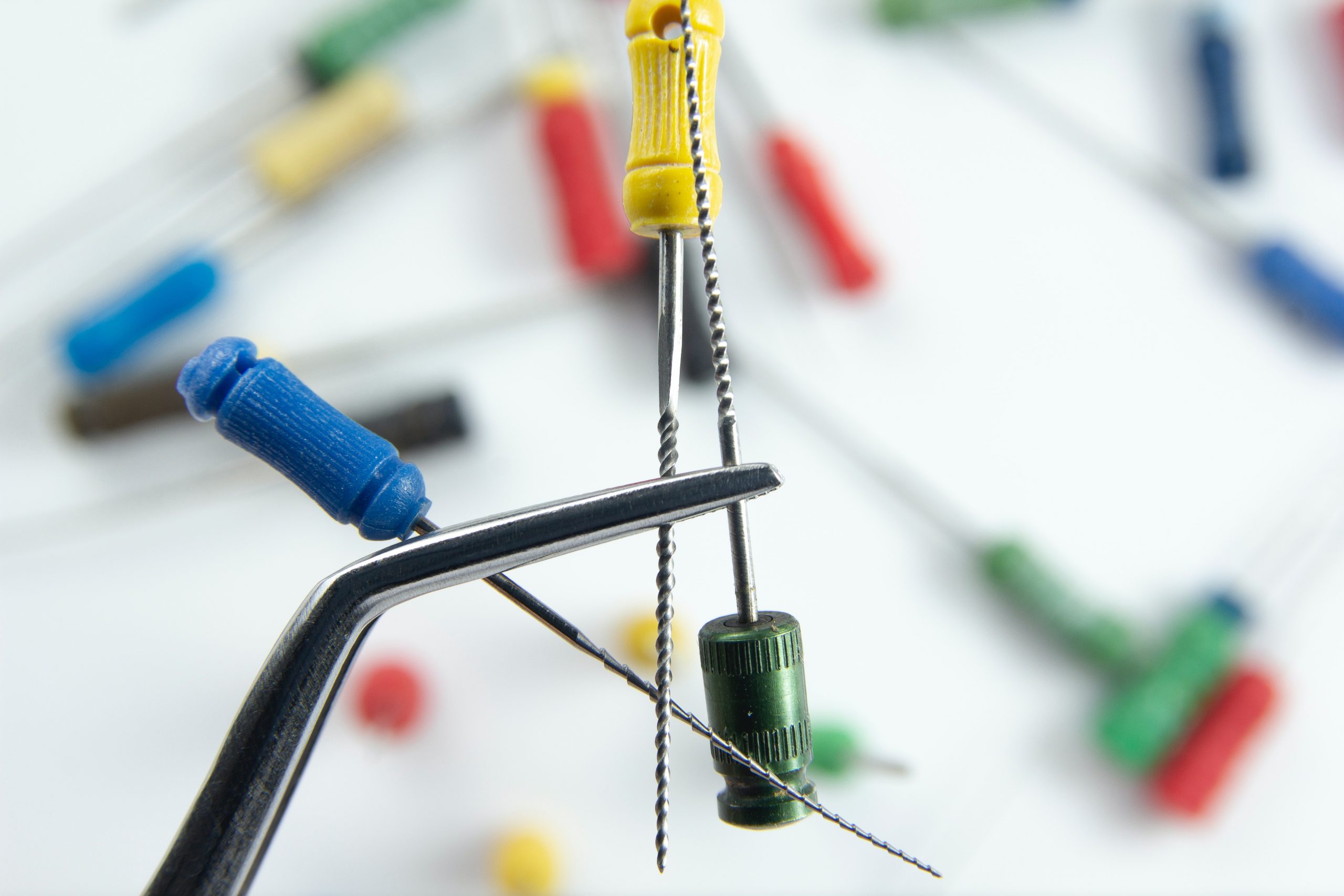
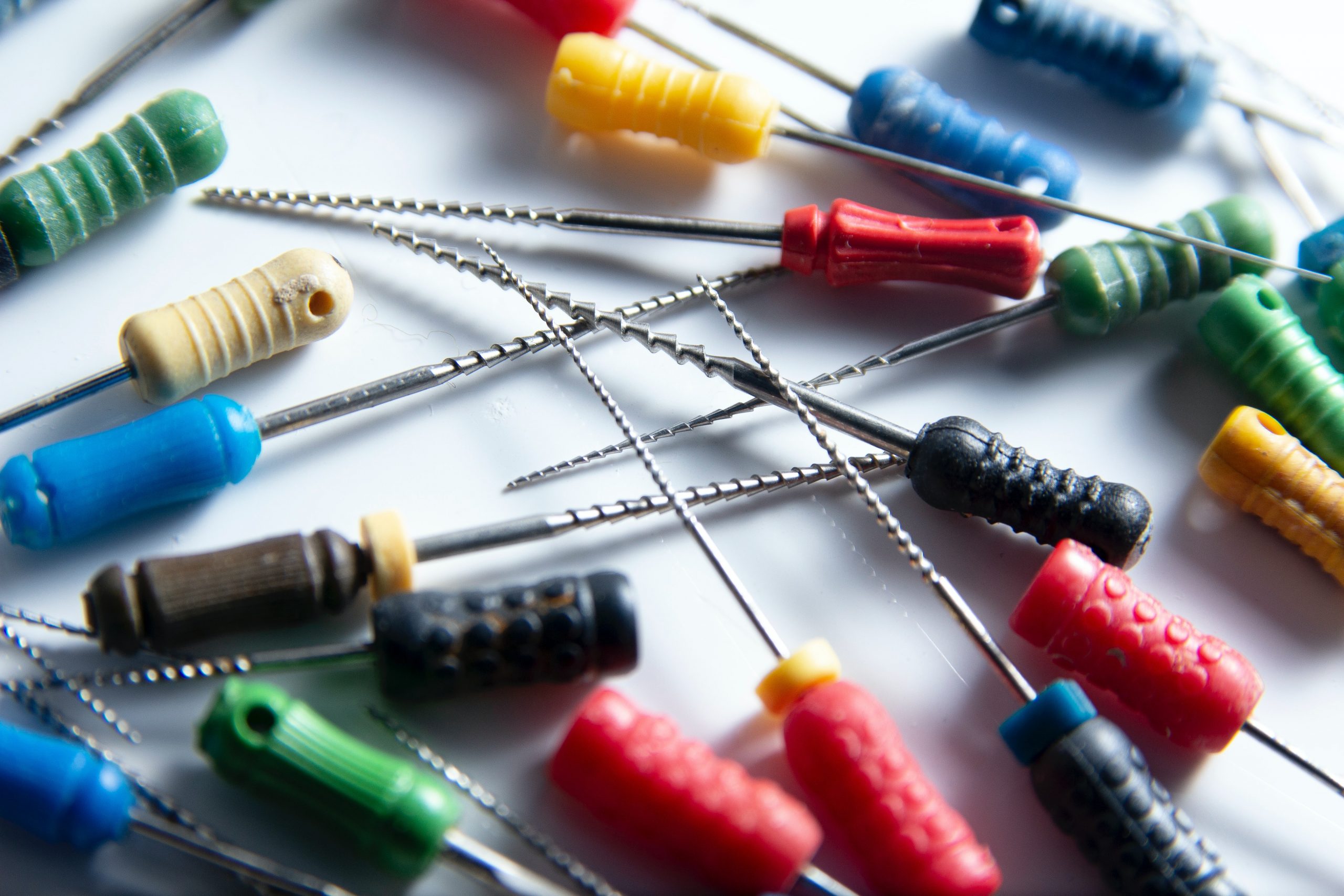
Instruments
1)Sybron Twist (TF) files are the workhorse of instrumentation. When using the "crown-down" technique, the 0.04mm file should reach most of the canals to maintain working length.
2)Basic Set: Endo-Plugger, Endo-Explorer , Endo Spreader; Rinse: Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl),2% Chlorhexidine
3)Thermal Condensation Stick with Gutta Percha
4)AH Plus Root Canal Sealer
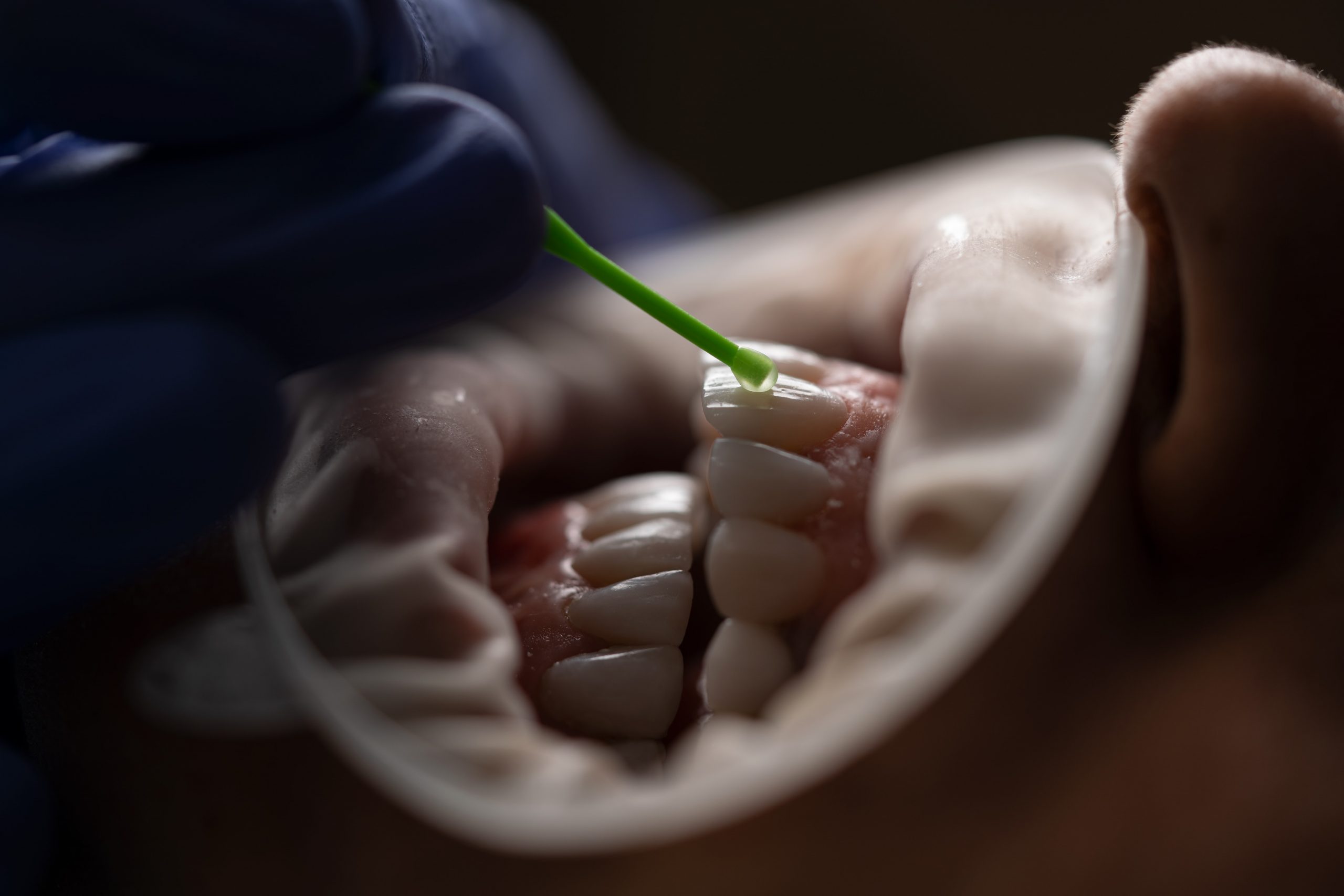
Root preparation techniques: It includes access, irrigation, obturation of the infected tooth.
1) Negotiation: After access in a straight line, it is necessary to fill the canal to traverse to see if the canal route is free and can be easily fixed.Ideally, negotiation is performed with small K files (6-8) used with gentle, passive insertion to define the curvature, length, calcification, and diameter of the canal.
2 ) Achieving permeability: Permeability is an extension of negotiations. Transparency refers to the ability to see a small K (6-10) through the apical opening about 1-2 mm. If the path of the canal through the apical foramen is not cleared, there is a risk that a "sludge pool" will form at the apex, which can create an unnecessary possibility of iatrogenic effects.
3) Creating a Glide Path: A glide path is a small handmade "debridement" that expands the canal to a size of about 15K.The endodontic literature agrees that creating a glide path is essential to reduce the frequency of separation of nickel-titanium rotary files.
4) Rotary files: Put simply, efficiency and attainment nothing can replace the best possible result with rotary instruments compared to Gates Glidden hand files and burs.
Root Canal complications
1) Root canal preparation error: This may be iatrogenic due to error in instrumentation
2)Root canal Blockage: Obstruction due to accumulation of residual tissues at the apical part of canal.
3)Hand instruments fracture: It can occur due to torsion stress.
4) Tooth fracture: Usually affects root / crown. Root canal fractures can occur when forces during the preparation is greater than the root canal wall.
Your mouth will be numb for several hours after the root canal treatment. Most people can return to work, school, or other activities immediately. You can wait for the numbness to pass before eating. Until the end of the root canal treatment with a permanent filling or crown, try not to chew on the tooth. This helps keep the area clean and can prevent a weak tooth from breaking before it can be fully restored.